In the dynamic world of fitness, circuit training has emerged as a powerful and efficient workout strategy. It combines cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and endurance within a structured format, offering a comprehensive approach to fitness. In this blog, we’ll explore the concept of circuit training, provide examples of effective circuit workouts, and offer nutrition guidelines to fuel your body for optimal performance and recovery.
Understanding Circuit Training:
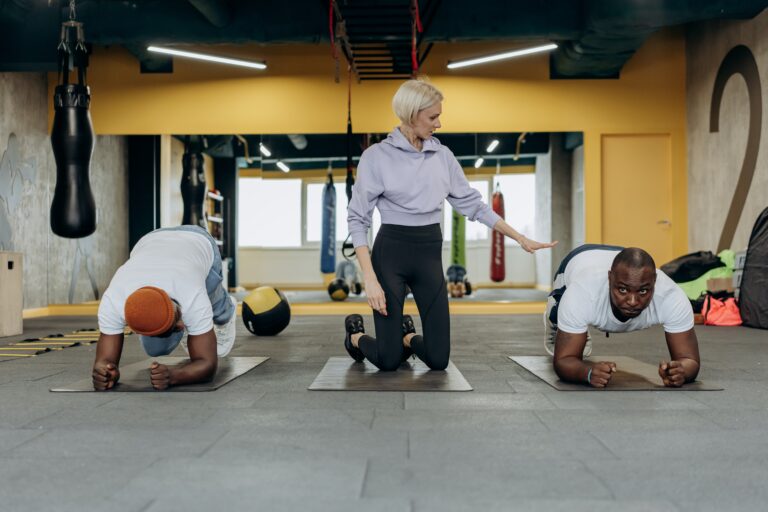
Circuit training involves a series of exercises performed consecutively with minimal rest in between. These circuits can target various muscle groups and incorporate both aerobic and anaerobic activities, making it an excellent choice for individuals looking to enhance overall fitness in a time-efficient manner.
Benefits of Circuit Training:
- Efficiency: Circuit training maximizes efficiency by combining various exercises in a single session. This approach allows you to achieve both cardiovascular and strength benefits in less time compared to traditional workout routines.
- Calorie Burn: The combination of resistance training and cardiovascular exercise in circuit training promotes calorie burn during and after the workout. This can contribute to weight management and fat loss goals.
- Versatility: Circuit training can be adapted to different fitness levels and goals. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced athlete, you can tailor the intensity and complexity of the circuits to match your fitness level.
- Increased Endurance: By incorporating cardiovascular exercises into the circuit, you improve your overall endurance. This can enhance your performance in various physical activities and daily tasks.
Circuit Training Examples:
- Full-Body Circuit:
- Jumping jacks: 1 minute
- Bodyweight squats: 1 minute
- Push-ups: 1 minute
- Plank: 1 minute
- Jump rope: 1 minute
- Strength and Cardio Circuit:
- Dumbbell lunges: 12 reps (each leg)
- Kettlebell swings: 15 reps
- Burpees: 10 reps
- Mountain climbers: 1 minute
- Core and Stability Circuit:
- Bicycle crunches: 20 reps (each side)
- Stability ball plank: 1 minute
- Russian twists: 15 reps (each side)
- Side plank: 30 seconds (each side)
Nutrition Guidelines for Circuit Training:
- Pre-Workout Fuel: Consume a balanced meal 2-3 hours before your circuit training session. Include complex carbohydrates (whole grains, fruits), lean proteins (chicken, fish, tofu), and a small amount of healthy fats (avocado, nuts) to provide sustained energy.
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated before, during, and after your workout. Dehydration can impair performance and hinder recovery. Aim to drink water consistently throughout the day.
- Post-Workout Nutrition: After completing your circuit, prioritize a post-workout meal or snack rich in protein and carbohydrates. This aids in muscle recovery and replenishes glycogen stores. Examples include a protein shake with a banana or Greek yogurt with berries.
- Nutrient Timing: Consider consuming a well-balanced meal within 1-2 hours of finishing your circuit training. This window is crucial for optimizing nutrient absorption and supporting muscle repair.
Conclusion:
Circuit training is a versatile and time-efficient approach to fitness that can be adapted to various goals and fitness levels. When combined with proper nutrition, the benefits of circuit training are amplified, leading to improved strength, endurance, and overall well-being. By incorporating these dynamic workouts into your routine and fueling your body with the right nutrients, you’ll unlock the potential for a healthier, fitter, and more energized version of yourself. Remember, consistency and a holistic approach are key to achieving lasting results.